
About BADEA
Who we are
The Arab Bank for Economic Development in Africa (BADEA)
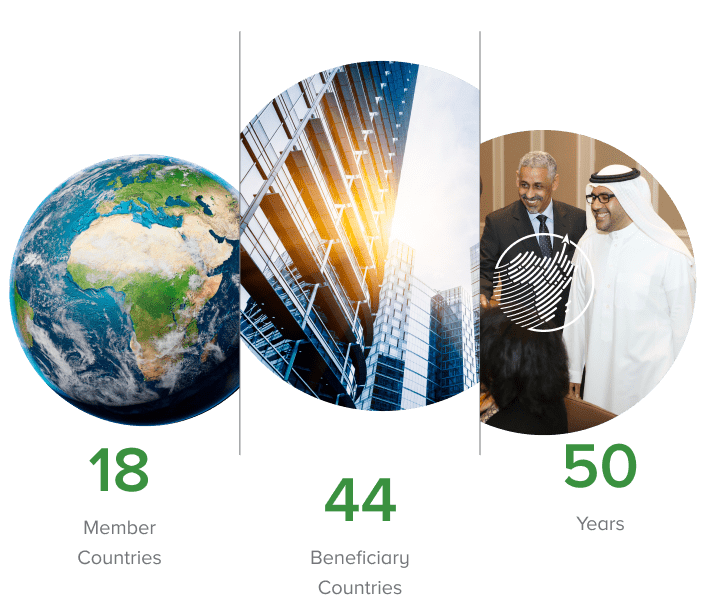
BADEA was established pursuant to the resolution of the 6th Arab Summit Conference held in Algiers on 28 November 1973, beginning operations in March 1975. The Bank is a development finance institution, owned by eighteen member countries of the League of Arab States which signed an establishment agreement on February 18, 1974.
BADEA is also an independent international institution with full administrative and financial autonomy.
It is governed by an establishment agreement and the principles of international law. Its headquarters are located in Khartoum, capital of the Republic of Sudan.

Our Mission
The Bank was established to strengthen economic, financial and technical cooperation between Arab and African countries, and to embody Arab-African solidarity on the basis of equality and friendship.
Accordingly, the Bank has been entrusted with a mandate to participate in financing the economic development of African countries stimulate the contribution of Arab capital to Africa’s development and provide the technical assistance necessary for Africa’s development. Projects financed by BADEA are of paramount importance to the beneficiary countries and are consistent with their economic development plans. In some cases, these projects are regional in nature and contribute to economic integration in the spirit of the African Union.
Public Sector Development Projects
Private Sector Operations
Trade Operations

Capacity Development Operations

Total Commitment Amount
BADEA in Numbers
Our Success Speaks Itself

Countries of Intervention
BADEA provides support to 44 African countries that are not members of the Arab League: Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Republic of Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo, Côte d’Ivoire, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Seychelles, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe.

